Ở bài Cấu trúc dữ liệu Set trong Python, các bạn đã tìm hiểu về Set. Trong bài này, chúng ta cùng xem xét một số thao tác có thể thực hiện trên Set trong Python.
1. Duyệt từng phần tử của Set
Sử dụng vòng lặp for để duyệt từng phần tử của Set trong Python.
my_set1 = {'gochocit', True, 5, 'com'}
print("my_set1:")
for x in my_set1:
print(x, end=' ')
my_set2 = {1, -7.5, 'hello', 1, 'hello'}
print("\nmy_set2:")
for x in my_set2:
print(x, end=' ')
Kết quả
my_set1:
True com 5 gochocit
my_set2:
1 -7.5 hello
2. Các toán tử trên Set
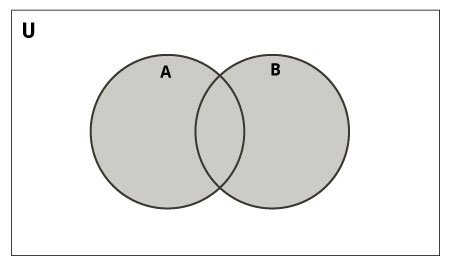
2.1. Toán tử Union
Phép kết hợp (union) 2 Set sẽ tạo ra một Set mới gồm tất cả các phần tử của cả 2 Set đó. Chúng ta có thể dùng toán tử | hoặc hàm union() để kết hợp 2 Set.
my_set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
my_set2 = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
# Union using operator |
my_set3 = my_set1 | my_set2
print("Union using operator |:", my_set3)
# Union using union()
my_set4 = my_set1.union(my_set2)
print("Union using union():", my_set4)
Kết quả
Union using operator |: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
Union using union(): {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
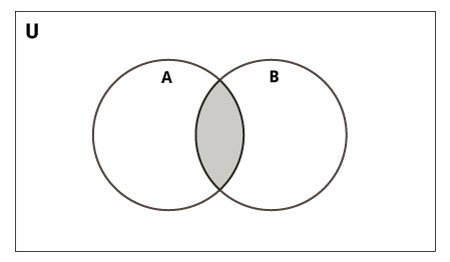
2.2. Toán tử Intersection
Phép giao (intersection) 2 Set sẽ tạo ra một Set mới chỉ gồm các phần tử thuộc cả 2 Set đó. Chúng ta có thể dùng toán tử & hoặc hàm intersection() để giao 2 Set.
my_set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
my_set2 = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
# Intersection using operator &
my_set3 = my_set1 & my_set2
print("Intersection using operator &:", my_set3)
# Intersection using intersection()
my_set4 = my_set1.intersection(my_set2)
print("Intersection using intersection():", my_set4)
Kết quả
Intersection using operator &: {4, 5}
Intersection using intersection(): {4, 5}
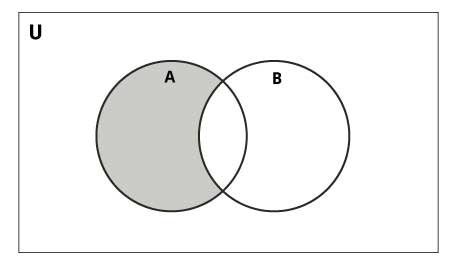
2.3. Toán tử Difference
Phép lấy phần khác nhau (difference) của 2 Set sẽ tạo ra một Set chỉ chứa các phần tử thuộc về một Set mà không thuộc về Set kia. Chúng ta có thể dùng toán tử – hoặc hàm difference() để giao 2 Set.
my_set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
my_set2 = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
# Difference using operator -
my_set3 = my_set1 - my_set2
print("Difference using operator -:", my_set3)
# Difference using difference()
my_set4 = my_set1.difference(my_set2)
print("Difference using difference():", my_set4)
Kết quả
Difference using operator -: {1, 2, 3}
Difference using difference(): {1, 2, 3}
2.4. Toán tử Symmetric Difference
Phép lấy phần khác nhau đối xứng (symmetric difference) của 2 Set sẽ tạo ra một Set chứa các phần tử không thuộc cả 2 Set. Chúng ta có thể dùng toán tử ^ hoặc hàm symmetric_difference() để giao 2 Set.
my_set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
my_set2 = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
# Symmetric Difference using operator ^
my_set3 = my_set1 ^ my_set2
print("Symmetric Difference using operator ^:", my_set3)
# Symmetric Difference using symmetric_difference()
my_set4 = my_set1.symmetric_difference(my_set2)
print("Symmetric Difference using symmetric_difference():", my_set4)
Kết quả
Symmetric Difference using operator ^: {1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}
Symmetric Difference using symmetric_difference(): {1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}
3. Các phương thức của Set
Python hỗ trợ nhiều method để giúp thao tác với Set dễ dàng hơn. Một số method thường sử dụng với Set được mô tả ở bảng bên dưới.
| Phương thức | Chức năng |
| add() | Thêm một phần tử vào set |
| clear() | Xóa tất cả phần tử từ set |
| copy() | Trả về một bản sao chép của set |
| difference() | Trả về một set chỉ chứa các phần tử thuộc về set 1 mà không thuộc set 2 |
| difference_update() | Xóa những phần tử của một set mà nằm trong một set khác |
| discard() | Xóa một phần tử cụ thể của set |
| intersection() | Trả về một set chỉ gồm các phần tử thuộc cả 2 set |
| intersection_update() | Xóa các phần tử của một set mà không nằm trong một set khác |
| isdisjoint() | Cho biết 2 set có các phần tử thuộc cả 2 set đó hay không |
| issubset() | Cho biết một set có nằm trong một set khác hay không |
| issuperset() | Cho biết một set có bao gồm một set khác hay không |
| pop() | Xóa một phần tử của set |
| remove() | Xóa một phần tử cụ thể của set |
| symmetric_difference() | Trả về một set chứa các phần tử vừa không thuộc set 1 vừa không thuộc set 2 |
| symmetric_difference_update() | Loại bỏ các phần tử thuộc cả 2 set ở set 1 rồi chèn các phần tử chỉ thuộc set 2 vào set 1 |
| union() | Trả về một set bao gồm tất cả các phần tử của 2 set |
| update() | Thêm tất cả phần tử của set 2 mà không thuộc set 1 vào cho set 1 |
Ví dụ sử dụng các method của Set
my_set1 = {'John', 'Marry', 'Henry'}
my_set2 = {'Kane', 'Cris', 'John'}
# add()
my_set1.add('Son')
print("add my_set1:", my_set1)
# clear()
my_set1.clear()
print("clear my_set1:", my_set1)
# copy()
my_set_copy = my_set2.copy()
print("copy my_set2:", my_set_copy)
# isdisjoint()
my_set1 = {'John', 'Marry', 'Henry'}
my_set2 = {'Kane', 'Cris', 'John'}
print("my_set1 havenot a intersection with my_set2?", my_set1.isdisjoint(my_set2))
my_set1 = {'John', 'Marry', 'Henry'}
my_set2 = {'Kane', 'Cris', 'Son'}
print("my_set1 havenot a intersection with my_set2?", my_set1.isdisjoint(my_set2))
# update()
my_set1.update(my_set2)
print("update my_set1:", my_set1)
Kết quả
add my_set1: {'Marry', 'Henry', 'Son', 'John'}
clear my_set1: set()
copy my_set2: {'Kane', 'Cris', 'John'}
my_set1 havenot a intersection with my_set2? False
my_set1 havenot a intersection with my_set2? True
update my_set1: {'Kane', 'Henry', 'John', 'Marry', 'Cris', 'Son'}